How do supply and demand work in economics?
The modern economy is built on demand and supply. Understanding these concepts is important for everyone, whether they are students learning the basics or policymakers making decisions that impact entire industries. This guide to how demand and supply actually work in the real world is important for all of them. It is for anyone who wants to know how markets work, whether they are an economist, an academic or just a general curiosity.
Table of Contents
ToggleYou’ll learn the basics but also gain a unique insight into how changes in demand and supply impact Everything from consumer behavior to global trade.
Understanding How Do Supply and Demand Work

Let’s begin with the basics.
What is Supply?
The supply is the amount of a service or product that a seller will and can provide within a certain timeframe at different prices. This is a key driver for the market and is determined by:
- Production costs: When production costs increase, the supply of goods generally decreases because it becomes less profitable for a business to produce goods.
- Technological Improvements: Emphasizes advanced technology production and supply
- Government policies: Subsidy and tax on goods can encourage and discourage supply
An example? Imagine a company that makes headphones. If manufacturing costs drop, the company can offer more headphones on the market because production is cheaper.
What is Demand?
Demand is the willingness and ability of the consumer to buy a product. It is driven by a number of factors, including:
- Income levels: In general, the more income a consumer has, the greater their demand for goods.
- Related Goods Prices: Demand for a product is often dependent on the prices of related goods.
- Consumer preferences: Trends and fads have a significant impact on demand.
If people develop a sudden taste for plant-based dairy products, their demand for cow’s milk could decrease.
Law of Supply and Demand
According to the law of supply and demand, these two forces work together to determine the market price of goods and services.
- Prices tend to increase when demand increases, but supply is constant.
- Prices usually fall when demand and supply are constant.
This simple law plays a key role in the dynamics of the market.
Market Equilibrium – Where Demand and Supply Meet
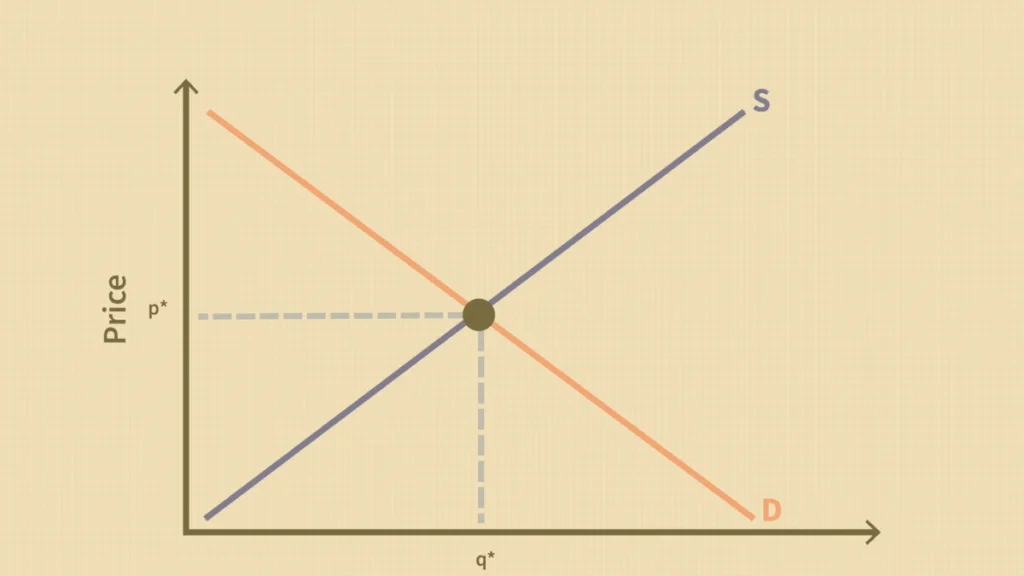
Market equilibrium is one of the most fascinating concepts in supply and demand.
What is market equilibrium?
The equilibrium point is where the supply and demand of goods are equal. There is no shortage or surplus at this point. This is the point where the price adjusts itself. At this place, the business does not make any profit or loss. At the equilibrium point, Everything remains constant and becomes equal.
For example: Imagine that a farmer is selling strawberries. They find that at $3 per basket, consumers will buy as many baskets as they can make. This $3 price is the equilibrium point of the market.
Surpluses and Shortages
Surpluses and shortages are created when markets are not in equilibrium.
- Surplus – When supply exceeds demand. A store may discount unsold winter coats after the end of a season.
- Shortage: When demand exceeds the supply. Imagine a concert ticket in high demand that is sold out.
The market is forced to adjust its price due to these imbalances.
Real-world Dynamics of Equilibrium
Markets rarely operate at equilibrium. Seasonality, consumer trends, and global events are all external factors that disturb market equilibrium. The global face mask shortage in 2020 due to the sudden increase in demand for masks due to the global pandemic is one of these. This is a great example; it was more than the supply.
The relationship between supply and demand
Understanding the interaction between supply and demand can give you a deeper understanding of markets. Let’s look at a few interesting dynamics.
Price Elasticity in Demand and Supply

This is a key concept that is important in understanding this relationship. It measures the sensitivity of supply and demand to changes in price.
- Elastic demand: A small change in price can cause a big change in demand (for example, luxury goods like designer handbags).
- Inelastic demand: When the price of a product increases, but there is little change in demand (for example, essential items like insulin).
Supply elasticity is a measure of how quickly producers can adjust their production to changes in pricing.
Shifting Curves
External influences can affect both the supply and demand curves.
- Shifting Demand: A new health study that reveals avocados as a superfood could increase demand even if the price remains unchanged. This causes the demand curve to shift upward.
- Shifts in Supply: New farming techniques could increase avocado production, shifting the curve downward.
These shifts ultimately disrupt the equilibrium of the market and cause price changes.
Feedback Loop of Expectations
How Expectation Impacts Markets This is a unique and overlooked aspect of supply and demand. If consumers expect inflation, such as price rises, demand can increase in anticipation, causing artificial shortages if producers anticipate price falls. If they do so, they may use their supply in advance, which may create an artificial shortage.
This feedback loop illustrates how psychological factors, such as anticipation and expectations, can have tangible effects on economic outcomes.
Applications in Real-Life Across Industries
Supply and demand principles are not only theoretical. They play out in all industries every day.
- Energy Sector: Global energy prices are affected by fluctuations in oil supply (due to geopolitical tensions).
- Retail Retailers set prices based on supply and demand during promotional periods or different seasons.
- Tech industry: When a new gadget is launched, the limited supply coupled with high demand can often drive up the initial price, creating exclusivity.
Understanding these applications can help bridge the gap between theory and practice by making economic principles more actionable.
The Economics of Supply and Demand
The concepts of supply and demand are not isolated. They underpin the functioning and development of economics and markets. Understanding these dynamics is important for understanding consumer choices, predicting market trends, and developing product pricing strategies.
These principles provide students and researchers with a strong base from which to build more complex economic principles. Supply and demand are used by businesses and policymakers to forecast trends and make decisions.
Harnessing this Knowledge
You probably have a good understanding of the complex dance between supply and demand. Understanding supply and demand is more than just learning the definitions. It’s about understanding how markets work and how pricing changes. Next time you buy gas. If you see a sudden rise in pricing or why coffee is more expensive today compared to last week, then you will be able to understand the dynamics of supply and demand.
There are many resources to help you deepen your understanding, whether you are a student of economics or a researcher who wants to learn more about theoretical frameworks or if your goal is to implement these theories into your business strategy. Understanding the demand can be a better decision for you, which will give you good guidance to make a better decision.

